Public health careers have projected a growth potential of 18 percent, which is why it’s such a hot topic. Within the careers in public health, there are specializations to consider. The areas of public health that are the most common include Environmental Health, Behavioral Science and Health Education, Health Services Administration, Biostatistics, and Epidemiology. When a healthcare professional is trying to determine which specialization will work best for their needs and long-term goals, it’s typically important to consider the Public Health areas of interest. Professionals gravitate toward the specialization areas that spark their interest the most. After all, who wants to dig deeper into a public health career that does not have the slightest fascination for them?
What are the 5 Core Disciplines of Public Health?
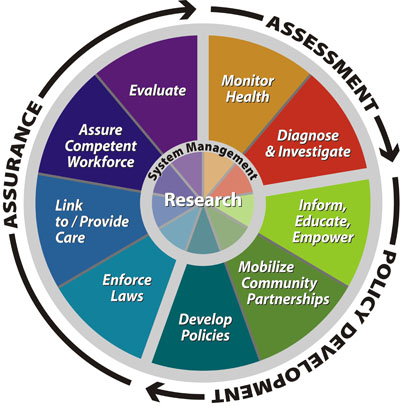
One of the key questions regarding careers in Public Health is: “What are the five core disciplines of public health?” It’s important to understand the basic disciplines, and then to see how those areas have evolved and expanded into other areas of Health Care and Patient Management. The five core disciplines of public health include Epidemiology, Health Promotion and Education, Biostatistics, Health Administration, and Environmental Health. These are the pillars of the industry. As the 5 core disciplines of public health, they are the core areas of Public Health. In an exploration of possible public health career opportunities, these 5 core areas of public health become the areas of most expansive growth and development. They are the touchstones out of which other focal areas may develop.
Source: CDC.gov
An examination of the five core disciplines of public health also highlights the key achievements and continued efforts to further push forward Public Health and Safety policy changes. The goals have seemed simple, but the solutions take time to implement, and the results don’t happen overnight. Over the last few decades, Public Health has made amazing strides in their efforts to reduce the number of people smoking, to eliminate unsafe working conditions, and to reduce the number of infectious diseases. On the flip side, Public Health officials foster programs that work toward safe and reliable food sources and distribution, with the continued efforts to encourage physical activity and reduce salt intake. The goal of medical and health officials is to increase the life expectancy of humans while focusing on improving the quality of life.
How Do I Choose an MPH Specialization?
The concentrations in Public Health involve the same basic target areas: Epidemiology, Health Promotion and Education, Biostatistics, Health Administration, and Environmental Health. The master’s in public health specializations touches upon aspects of Disaster Management and Emergency Preparedness, as well as aspects of International Public Health Management. As Global Health initiatives continue to touch everyone at such a granular level, technological innovation inspires new sharing and distribution of information and resources around the globe. The world has become so much smaller and closer to home from a strategic intervention and improvement perspective.
The key areas of specialization in Public Health involve an exploration of Biostatistics and Epidemiology concentration, with emphasis on health trends and statistical methodologies. Medical professionals need to determine what happened in the past so that they can prepare for and even prevent future disease outbreaks. These career opportunities require a focus on analytics and research, so those who pursue a master of Public Health specializations in these areas are adept at brainstorming and evaluating the data sets while understanding the real-time implications of how the statistics will affect a population.
While numbers and statistics will always have an important place in master’s in public health specializations, communication plays a key role. Community health promotion, in particular, allows medical professionals to educate and empower communities to initiate changes that will affect them on an individual and community health level. With these education initiatives, the community is inspired to make changes to their personal activity levels, salt intake, smoking cessation, immunization, and every other aspect that has brought about a healthier and longer-living population. The Health Promotion and Education concentration offers the framework by which medical professionals with a MPH degree can build upon the evaluation, communication, and intervention skills they’ve learned in the program.
Global Health is at the root of many of the masters in Public Health concentrations in one way or another. With so much of Public Health now taking on international significance, medical professionals must understand how policies and even communication and promotion strategies will play out against the grander scheme of socioeconomic and cultural concerns.

The Most Common Concentrations in Public Health
Biostatistics
Biostatistics is a combination of Bio + statistics. In practice, medical professionals gather and analyze the data, which they then use to interpret and make predictions. An MPH in Biostatistics benefits from a strong background in statistics and mathematical processes, but a career in this field can also rely heavily on scientists and statisticians to work in collaboration. Biostatistics can also be part of research studies, where the medical professional develops a clinical trial, monitor the results, and then write up their findings in scientific papers to inform the greater scientific and medical community of the results.
Child & Maternal Health
Child & Maternal Health involves the most vulnerable population, so it’s a main focus of national and international health initiatives. The focus of this specialization is for medical professionals to understand and seek to protect women, children, and families in the US and around the world. A primary goal of this concentration is to identify health risks and mitigate the circumstances that lead to future health problems for at-risk populations.
Community Health
Community Health specializations focus on how to protect and improve the health and outcomes of the community members as a whole. Instead of focuses just on the most vulnerable populations, but it can highlight overarching issues that are affecting large portions of the community. While some concerns like child abuse, neglect, domestic abuse, crime, polluted drinking water, addiction, poverty, inequality, health disparity, and environmental contamination overlap with other areas of specialization, there are more overarching themes and concerns with a Community Health concentration.
Environmental Health
Environmental Health focuses on the natural and developed environment, with specific attention to how it can affect the mental and physical health of a population. This specialization takes into account how contamination and exposure to hazardous substances affect public health issues. It can also explore issues of climate change and other environmentally impactful disturbances including hazards that are chemical, physical, cultural, and biological in nature. CDC’s National Center for Environmental Health (NCEH) is tasked with protecting the American people against environmental dangers.
Epidemiology/Infectious Disease
Epidemiology/Infectious Disease involves the study of viruses and contagious diseases like polio, smallpox, or typhoid. While many of the most infectious diseases are largely under control in developed countries like the US, medical professionals must be constantly vigilant to avoid new threats from taking hold with dire consequences. Epidemiology and Infectious disease are also essential for global health services since vaccinations are not as wide-spread or accessible in international populations. The study of possible causes for disease and outbreaks also has cross-over with Environmental Health concentrations, since contamination and toxic influences can affect the development of a disease cluster of cancer or other non-contagious diseases.
Global Health
Global Health focuses on the health of global populations. The goal is to improve health and equity situations while working through some of the most widespread issues inherent on the international stage. Issues like poverty, racism, war-torn communities, contaminated water, family planning, and so many other public health policies are part of the global health discussion. The CDC has been working on global health projects for more than 60 years., with a focus on protecting Americans while helping the international community detect, prevent, and address health concerns.
Health and Human Services
Health and Human Services is a department in the US government that protects Americans while working to improve their lives. The focus of this concentration is to support medical and health advances that will positively impact the lives of US citizens, with international ramifications and ripple effects on the work.
Nutrition
Nutrition focuses on nutritious and nutrient-rich food that nourishes and contributes to a healthier population both in the US and around the world. Nutrition involves the intake of fat, carbohydrates, and protein. It also focuses on how a healthy diet contributes to a longer and more productive life. Nutrition is involved in many of the health-related disciplines both for US-based and international concerns.
Occupational Health
Occupational Health covers the on-the-job dimensions. As a concentration, Occupational Health involves the identification of risks that endanger the health and safety of workers. It can involve environmental health concerns since it often delves into training, protection, and safe removal of dangerous hazards from the workplace. It can also involve training workers in disaster preparedness and response efforts.
Social and Behavioral Science
Social and Behavioral Science is a concentration that can be related to social services, teaching, or counseling. It involves an exploration of what it means to be human, and what fundamental behaviors, actions, or interactions might come into play based on a specific stimulus. By understanding why people act or react the way they do, medical professionals can better prepare themselves to mitigate unforeseen circumstances. This focal area has lots of (cross-over) with other disciplines since the psychological aspects of how humans will respond is an important consideration in almost every area of public health and safety.
Related Rankings:
Top 10 Maternal and Child Health MPH Programs
Top 25 Online MPH Community Health Degree Programs
Top 10 MPH Environmental Health Degree Online Programs
Top 25 Online MPH in Epidemiology